4838 Richard Road SW, Suite 400 | Calgary, AB, Canada T3E 6L1
Telephone: 403.910.1000
ATP | Process Flow Schematics and Diagrams
A horizontal, rotating vessel, the ATP Processor has individual zones in which the process steps occur to separate and recover the various product streams.
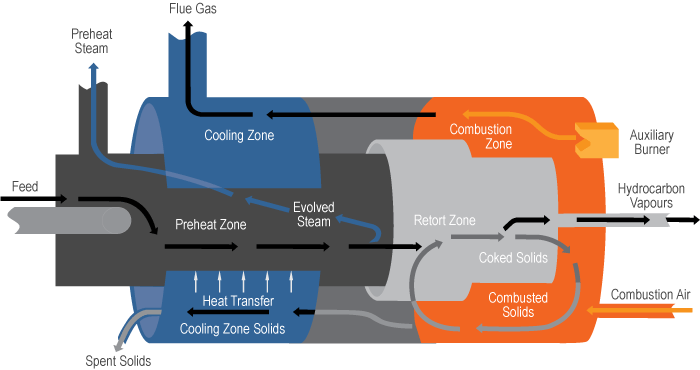
The Preheat Zone
- Feed material is heated and dried by transfer of heat from processed, out-going hot spent solids and combustion flue gases flowing through the Cooling Zone.
- Lumpy and frozen feed materials are ablated.
- Connate water is evaporated and the resulting steam prevents air from entering the Processor with the feed.
- Evolved steam is cooled outside the Processor where condensed water and possibly some trace hydrocarbons are recovered.
- Oversize material and rocks are removed.
The Retort Zone
- Preheated dry feed mixes with hot solids recycled from the Combustion Zone to rapidly achieve reaction temperatures.
- The resulting mix temperature volatilizes or thermally cracks the feed organics in an oxygen deficient atmosphere, yielding hydrocarbon vapour, and coke-coated solid particles.
- A concentrated stream of hot hydrocarbon vapours at reaction zone temperature is extracted from the Processor and processed externally.
- Spent solids and coke are discharged to the combustion zone.
Note - The hydrocarbon vapour is cooled outside the Processor; condensed product oil is recovered and may be directly fed to secondary treatment (hydrotreated) or pipelined. Concentrated light hydrocarbon gases are available for further processing and sold as products.
The Combustion Zone
- Air is added to burn the coke-coated solids entering from the reaction zone, heating the solids in the combustion zone.
- Auxiliary burners supply additional heat if required, such as for start up.
- A portion of the hot solids in the Combustion Zone are recycled to the Retort Zone.
- The balance of the solids and the combustion flue gases flow to the Cooling Zone.
Note - The combustion of coke usually provides the heat required for the process.
The Cooling Zone
- The entering hot solids and flue gases are cooled by indirect heat transfer to the incoming fresh feed in the Preheat Zone.
- The hydrocarbon-free solids are discharged and transported for disposal to mined out pit areas or other landfill. Spent shale is moistened for dust control, but no wet tailings ponds are required.
- Flue gases are discharged via a treatment system for removal of fine solids, acid gases, and other contaminants as required to meet environmental criteria.
